-
Posted on: 21 Dec 2022
-
Your creditworthiness is determined by a FICO and a credit score, but their calculations weigh different elements. So, before deciding, know the difference between FICO score and credit score. Your credit score is based on the risk characteristics of all customers; your Fico score is based on data from your credit report. Understanding the variations between these two scores will enable you to know why your credit could be less than you would have anticipated or what you need to do to raise it.
Should you have ever sought a loan, you most likely had to submit your FICO score. But what is a FICO score, and how does it differ from a credit score? How does the FICO score from the credit score? We will dissect the variations between these two scores in this article and discuss why both of them are significant. Knowing the variations between credit scores and FICO can help you ensure your next loan rate is the best one.
What is a FICO Score, and how does it work?
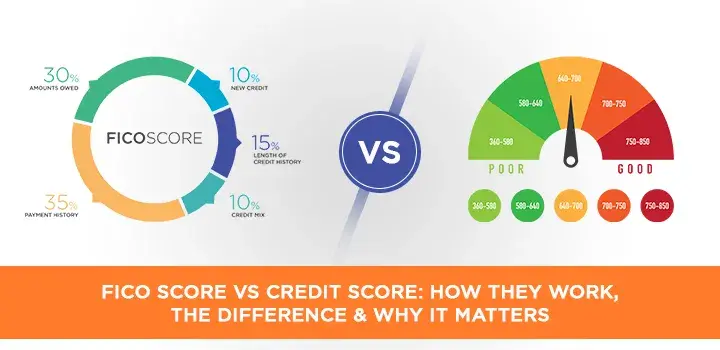
A Fico score—which is three digits—is supposed to show your creditworthiness. Built by Fair, Isaac Corporation, it is used by lenders during loan or credit card application processing. The score considers your payment history, debt level, and credit length, as well as other elements. Your Fico score may run from 300 to 850; the higher it is, the more likely you are to get accepted for a credit card or loan. Understanding your FICO score and acting to raise it can enable you to get authorized for goods with better terms and save on interest payments.
How is your FICO Score calculated?
Lenders evaluate a borrower's creditworthiness using a credit score known as the FICO score.
Examining your credit history can help you determine a FICO Score between 300 and 850; 850 is the best.
FICO Scores are based on five factors:
-
- Payment History (35%)
- 30% Amounts Owed
- 15% credit history length
- Fresh Credit (10%)
- What are the ten percent of types of credit used?
Why is your Fico Score important?
One of the most crucial elements the lender will take into account when you apply for a loan is your credit score. Your FICO score gauges your likelihood of debt repayment and runs from 300 to 850. While a low Fico score can indicate that you won't be authorized for a loan at all, a high Fico score might assist you in getting a cheaper loan interest rate. How, therefore, can you ensure that your FICO score is as high as it may be?
How can you improve your FICO Score?
Your Fico Score is crucial. One of the things lenders assess when deciding whether to approve your credit card or loan application. You should make sure your score is as high as it can be. These pointers help you raise your FICO Score.
- Check your credit report for mistakes and correct them
- Pay your bills on time
- Keep your credit utilization low - don't max out your credit cards
- Don't apply for too many new credit cards at once
- Don't close old accounts, especially if they have a long history of good payment behavior.
- Don't make too many big purchases in a short period
What are some of the factors that affect your FICO Score?
- Payment history: whether or not you have paid your bills on time;
- Amounts Owed: Compare your credit to your debt.
- Credit history length: the length of time you have held open credit accounts for
- New credit: requesting new lines of credit might drop your score.
- Kind of credit used: optimum combination of home loans, revolving lines of credit, and installment loans.
- Using a large proportion of your accessible credit will lower your score.
What is a Credit Score and how does it work?
Define a credit score here. A credit score is a number that represents your credit history and indicates to lenders your debt repayment ability. Your credit score falls between 300 and 850; the better interest rate you will probably get on a loan or mortgage, the higher your score. Five elements—payment history, debt level, credit history length, new credit inquiries, and kind of credit used—formulate your credit score.
How is your credit score calculated, and how can to improve your credit score?
Though many individuals have no idea how credit scores are computed, knowing the procedure can help you control your credit and raise your score. Though other credit scoring systems are now in use, the FICO score is the most often used one. Five elements define this score:
- One's payment history (35%).
- 30% Credit Utilization
- Credit Records (15%)
- Credit Mix, 10%
- Ten percent fresh credit
Your credit score is most importantly determined by payment history, as you can see. Keeping your credit card balances low and making all your payments on time is, therefore, rather crucial. These easy guidelines can help you start along the road toward financial success and assist you in improving your credit score.
The benefits of having a good credit score
Lenders use a credit score—a number—to assess a potential borrower's creditworthiness. Information from credit reports—kept by credit bureaus—helps to determine a credit score. Credit scores range from 300 to 850; the higher the number, the better. A decent credit score may rescue debtors. Interest on a debt runs thousands of dollars throughout its lifetime. On a $20,000 loan, a borrower with a credit score of 780, for instance, could anticipate paying around $300 less in interest than a borrower with a credit score of 680. Apart from reduced interest rates, strong credit may also result in quicker loan and credit card acceptance, as well as improved conditions on insurance plans. Everyone who wants to access reasonably priced borrowing needs a decent credit score.
What happens if you don't have a good credit score?
Less favorable loan conditions and a higher interest rate might follow from a poor credit score. Occasionally, you could not be authorized for a loan at all. Information from your credit report—including credit mix, credit use, and payment history—helps determine your credit score. You reduce the risk you present to lenders the better your credit score. If your credit score is poor, you may want to look at strategies for raising it before a loan application. Many tools abound to assist you in grasping and raising your credit score.
Why your credit score matters for more than just getting a loan or mortgage
Most individuals know that obtaining a loan or a mortgage requires their credit score to be taken into consideration. Still, credit ratings may affect many spheres of your life. For instance, insurance costs are sometimes set in part on your credit score. Most landlords will review your credit score throughout the screening process if you are renting an apartment. You should keep a decent credit score even if you do not intend to apply for credit anytime soon. How, then, is your credit score computed? The answer is straightforward: the data on your credit report determines your credit score. This covers elements such as credit use percentage, outstanding debt, and payment history. Keeping a clean credit record can assist you in guaranteeing a decent credit score, which will help you save money and reduce stress downstream.
Tips for maintaining a good credit score over time
Having a poor credit score indicates that you have not historically handled your credit effectively. Your credit score may be raised in numerous ways. The three credit bureaus provide a copy of your credit report, which you may review for mistakes. If you don't need additional credit lines, you may also keep your credit balances low, start paying your payments on time, and avoid creating new lines. Over time, these actions help you raise your credit score.
FICO score vs. Vantage Score
Lenders in the United States mostly employ two credit scoring systems: the VantageScore® and the FICO score. Though there are some significant variations to be aware of, both approaches compute a score using comparable information.
Originally adopted in 1989, the FICO score is the most often utilized credit score today. It runs from 300 to 850; a higher number denotes improved credibility. Five elements form the FICO score: payment history (35%), credit usage (30%), duration of credit history (15%), categories of credit utilized (10%), and current credit activity (10%).
Introduced in 2006, the Vantage Score® is progressively being accepted by banks. Like the FICO score, it runs from 300 to 850 but employs a distinct rating algorithm. Six elements form the VantageScore®: payment history (40%), age and kind of credit (21%), use patterns (20%), balances (11%), Available Credit (5%), and recent queries (3%). Your VantageScore® can be greater or lower than the FICO score, based on the lender.
When it comes to loans and other credit approvals, the FICO score and the VantageScore® are both crucial. Knowing both models is crucial, as lenders usually consider both scores when deciding what to do. Ask your lender for more information should you have queries about your score.
Conclusion:
In Conclusion, lenders evaluate a FICO score and credit score as crucial determinants of a loan or line of credit application. One must grasp the variations between the two and their respective operations. Strong credit may help you negotiate more effectively when it comes time to apply for a loan and save you interest costs.
If you have any questions about your FICO score vs credit score, don't hesitate to give us a call at (888) 803-7889.
Faq
1. What is the main difference between a FICO Score and a credit score?
A FICO Score is a specific type of credit score created by the Fair Isaac Corporation, while “credit score” is a general term that refers to any numerical representation of your creditworthiness. In short, all FICO Scores are credit scores, but not all credit scores are FICO Scores.
2. Which credit score do lenders use most often—FICO or others?
Most lenders prefer FICO Scores, as they are the industry standard used by about 90% of top U.S. lenders. However, some lenders also use VantageScore, another popular scoring model developed by the three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion).
3. How are FICO Scores and VantageScores calculated differently?
While both use similar factors—payment history, credit utilization, credit age, new credit, and credit mix—they weigh them differently. For example, FICO places more emphasis on payment history (35%), while VantageScore gives slightly more weight to recent credit behavior and total balances.
4. Can your FICO Score and credit score be different?
Yes. Since different scoring models and bureaus use varied algorithms, your FICO Score might differ from your VantageScore or other credit scores. It’s normal to see variations of 10–50 points depending on which bureau or model is used.
5. Which score should I monitor to understand my credit health?
If you’re planning to apply for a loan, mortgage, or credit card, monitor your FICO Score, as that’s the one most lenders check. However, keeping an eye on your VantageScore can still help you track general trends in your credit health.
-